
ISRO will launch communication satellite GSAT-6A on Thursday, March 29, 2018 at 4:56 pm IST
New Delhi:
The Indian Space Research Organisation or ISRO will launch its latest communication satellite - GSAT-6A on Thursday, March 29, 2018. The launch will happen from the Satish Dhawan Space Centre in Andhra Pradesh's Sriharikota at 16:56 hrs (4:56 pm) IST. Like its predecessor GSAT-6, the GSAT-6A too, is a high power S-band communication satellite.
What Is The GSAT-6A Satellite? And What Is Its Purpose?
The GSAT-6A is a high power S-band communication satellite. It will be India's second predominantly S-band communications satellite - first being the GSAT-6. It will complement GSAT-6, which has been orbiting Earth since August 2015 at 83 degrees East longitude. The purpose of the satellite is provide a platform for developing technologies such as demonstration of 6m S-Band 'Unfurlable Antenna', handheld ground terminals and network management techniques. These are useful in satellite-based mobile communication applications. The GSAT-6A launch will be ISRO's last launch for the financial year 2017-18. ISRO Chairman K Sivan has confirmed that the GSAT-6A launch would be followed by the launch of a navigation satellite which will be in the next fiscal.
 What Will Be The Lifespan Of The GSAT-6A Mission? And What Is The Cost Of The Project?
What Will Be The Lifespan Of The GSAT-6A Mission? And What Is The Cost Of The Project?
ISRO has stated that the life span of the GSAT-6A mission will be around 10 years. The cost of the 2-tonne satellite is approximately rupees 270 crores.
What Is An 'Unfurlable Antenna'? What Does It Do?
ISRO's 'unfurlable antenna' is a six-meter-wide antenna which looks somewhat like an umbrella. This will be 'unfurled' once the GSAT-6A satellite has been put in orbit. This antenna, specially designed for the mission, is three times as broad as the antennas that are usually used by ISRO. This antenna will allow mobile communication from anywhere via hand-held ground terminals. Apart from communications, the GSAT-6A satellite is believed to be designated for military use as well.
What Is S-Band? How Is It Useful?
S-band is an electromagnetic spectrum covering frequencies from 2 to 4 gigahertz (GHz). It crosses the conventional boundary between the Ultra High Frequency (UHF) and Super High Frequency (SHF) bands at 3.0 GHz. S-band is used by weather radars, surface ship radar, and some communications satellites. S-band is very useful because the 2.5 Ghz band is used globally for 4G services, and is worth billions of dollars. The S-band spectrum is extremely valuable for mobile broadband services.
What Are Some Of The Salient Features Of The GSAT-6A Satellite?
It will help provide mobile communication for India through multi-beam coverage facility. It will have S-band in five spot beams and C-band in one beam. It will have a 6m diameter 'unfurlable antenna' for user communication link. It also has a 0.8m fixed antenna for hub communication link. The overall size of the GSAT-6A satellite is 1.53m X 1.65 m X 2.4 m.
 How Will The GSAT-6A Be Launched? Which Rocket Will Carry The Satellite?
How Will The GSAT-6A Be Launched? Which Rocket Will Carry The Satellite?
The GSAT-6A communication satellite will be launched by ISRO's GSLV-F08 rocket. The GSLV-F08 will be the twelfth flight of Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle, and the sixth flight which will have an indigenous Cryogenic Stage. The launch of the GSLV-F08 rocket carrying the GSAT-6A will happen from the second launch pad at Sriharikota spaceport. The height of the rocket carrying the GSAT-6A is 49.1 metres and the weight is 415.6 tonnes.
How Many Stages Will The GSAT-6A Launch Comprise Of?
The GSAT-6A launch will have three stages (Stage 1, 2, 3) and end with the 'payload fairing'. 'Stage One' will comprise of two propellants - Earth storable liquid propellants and Composite solid propellant. 'Stage Two' will comprise of Earth storable liquid propellants, while 'State Three' will have Cryogenic propellants.
 How Long Will It Take For The GSAT-6A Satellite To Be Put In Orbit?
How Long Will It Take For The GSAT-6A Satellite To Be Put In Orbit?
The total time to put the GSAT-6A satellite in orbit since its blast off from the launch pad in Sriharikota will be 17 minutes and 46.50 seconds.
 What Are The Technological Details Of The GSAT-6A Launch?
What Are The Technological Details Of The GSAT-6A Launch?
The targeted Geosynchronous Transfer Orbit or GTO of the GSLV-F08 include a 'perigee' (point in the orbit of a satellite at which it is nearest to the earth) of 170 kilometres, an 'apogee' (point in the orbit of a satellite at which it is farthest from the earth) of 35,975 kilometres, an 'inclination' of 20.63 degrees, and an 'azimuth' of 108 degrees. The mission will include three orbit raising manoeuvres using the satellite's onboard propulsion system. The targeted orbit of the GSAT-6A is aimed at 36,000 kilometres. It will have a geostationary orbit at an inclination of zero degrees once in place over the 83 degree east longitude.
Understanding The GSLV or Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle Being Used For The GSAT-6A Mission
The Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle Mark II (GSLV Mk II) is the largest launch vehicle developed by India, which is currently in operation. This fourth generation launch vehicle is a three stage vehicle with four liquid strap-ons. The indigenously developed cryogenic Upper Stage (CUS), which is flight proven, forms the third stage of GSLV Mk II. From January 2014, the vehicle has achieved four consecutive successes.
What Is The GSAT-6A Satellite? And What Is Its Purpose?
The GSAT-6A is a high power S-band communication satellite. It will be India's second predominantly S-band communications satellite - first being the GSAT-6. It will complement GSAT-6, which has been orbiting Earth since August 2015 at 83 degrees East longitude. The purpose of the satellite is provide a platform for developing technologies such as demonstration of 6m S-Band 'Unfurlable Antenna', handheld ground terminals and network management techniques. These are useful in satellite-based mobile communication applications. The GSAT-6A launch will be ISRO's last launch for the financial year 2017-18. ISRO Chairman K Sivan has confirmed that the GSAT-6A launch would be followed by the launch of a navigation satellite which will be in the next fiscal.

ISRO's GSAT-6A satellite, once placed in orbit, will also benefit the armed forces
ISRO has stated that the life span of the GSAT-6A mission will be around 10 years. The cost of the 2-tonne satellite is approximately rupees 270 crores.
What Is An 'Unfurlable Antenna'? What Does It Do?
ISRO's 'unfurlable antenna' is a six-meter-wide antenna which looks somewhat like an umbrella. This will be 'unfurled' once the GSAT-6A satellite has been put in orbit. This antenna, specially designed for the mission, is three times as broad as the antennas that are usually used by ISRO. This antenna will allow mobile communication from anywhere via hand-held ground terminals. Apart from communications, the GSAT-6A satellite is believed to be designated for military use as well.
What Is S-Band? How Is It Useful?
S-band is an electromagnetic spectrum covering frequencies from 2 to 4 gigahertz (GHz). It crosses the conventional boundary between the Ultra High Frequency (UHF) and Super High Frequency (SHF) bands at 3.0 GHz. S-band is used by weather radars, surface ship radar, and some communications satellites. S-band is very useful because the 2.5 Ghz band is used globally for 4G services, and is worth billions of dollars. The S-band spectrum is extremely valuable for mobile broadband services.
What Are Some Of The Salient Features Of The GSAT-6A Satellite?
It will help provide mobile communication for India through multi-beam coverage facility. It will have S-band in five spot beams and C-band in one beam. It will have a 6m diameter 'unfurlable antenna' for user communication link. It also has a 0.8m fixed antenna for hub communication link. The overall size of the GSAT-6A satellite is 1.53m X 1.65 m X 2.4 m.
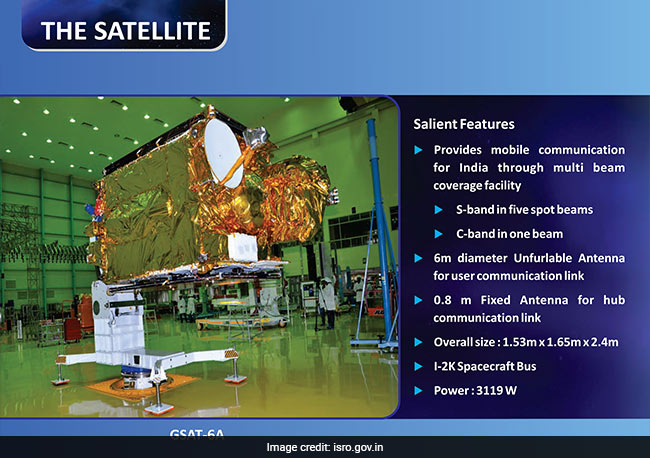
Some of the features of ISRO's GSAT-6A communication satellite
The GSAT-6A communication satellite will be launched by ISRO's GSLV-F08 rocket. The GSLV-F08 will be the twelfth flight of Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle, and the sixth flight which will have an indigenous Cryogenic Stage. The launch of the GSLV-F08 rocket carrying the GSAT-6A will happen from the second launch pad at Sriharikota spaceport. The height of the rocket carrying the GSAT-6A is 49.1 metres and the weight is 415.6 tonnes.
How Many Stages Will The GSAT-6A Launch Comprise Of?
The GSAT-6A launch will have three stages (Stage 1, 2, 3) and end with the 'payload fairing'. 'Stage One' will comprise of two propellants - Earth storable liquid propellants and Composite solid propellant. 'Stage Two' will comprise of Earth storable liquid propellants, while 'State Three' will have Cryogenic propellants.
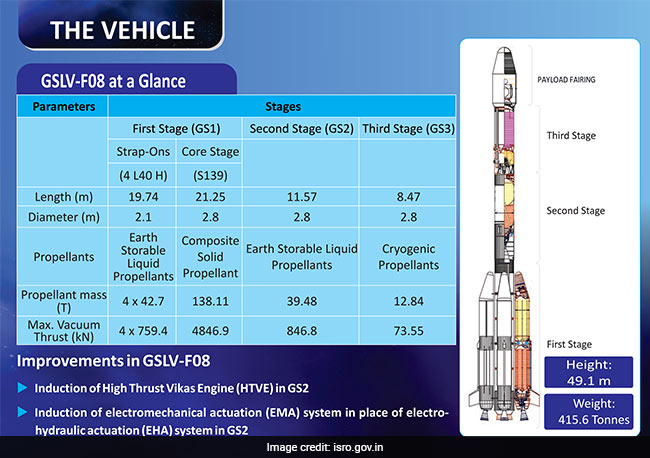
The different stages of the GSLV rocket which will carry the GSAT-6A satellite on board
The total time to put the GSAT-6A satellite in orbit since its blast off from the launch pad in Sriharikota will be 17 minutes and 46.50 seconds.
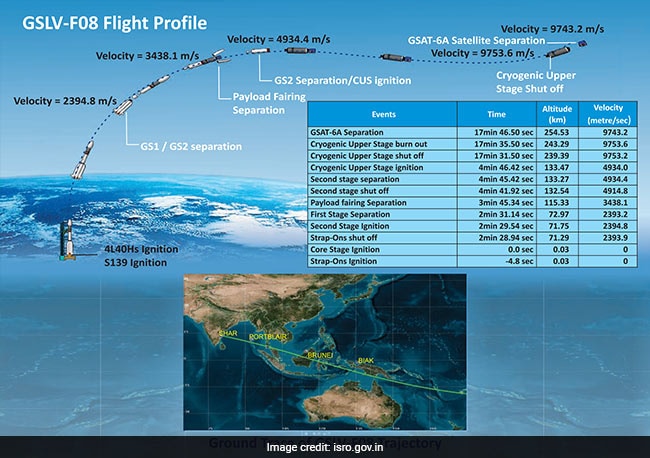
The flight path and profile of the GSLV-F08 - the rocket that will carry the GSAT-6A satellite
The targeted Geosynchronous Transfer Orbit or GTO of the GSLV-F08 include a 'perigee' (point in the orbit of a satellite at which it is nearest to the earth) of 170 kilometres, an 'apogee' (point in the orbit of a satellite at which it is farthest from the earth) of 35,975 kilometres, an 'inclination' of 20.63 degrees, and an 'azimuth' of 108 degrees. The mission will include three orbit raising manoeuvres using the satellite's onboard propulsion system. The targeted orbit of the GSAT-6A is aimed at 36,000 kilometres. It will have a geostationary orbit at an inclination of zero degrees once in place over the 83 degree east longitude.
Understanding The GSLV or Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle Being Used For The GSAT-6A Mission
The Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle Mark II (GSLV Mk II) is the largest launch vehicle developed by India, which is currently in operation. This fourth generation launch vehicle is a three stage vehicle with four liquid strap-ons. The indigenously developed cryogenic Upper Stage (CUS), which is flight proven, forms the third stage of GSLV Mk II. From January 2014, the vehicle has achieved four consecutive successes.
Track Latest News Live on NDTV.com and get news updates from India and around the world

