
GST will subsume a number of central and state taxes
The government is set to roll out GST or Goods and Services Tax from July 1. Touted as the biggest reform since Independence, the incoming indirect tax regime - GST - will subsume a variety of central and state levies. With GST, the government aims to create a common market, preventing 'tax-on-tax' and making goods and services cheaper. The GST Council, chaired by Finance Minister Arun Jaitley and comprising state counterparts, last week revised rates on 66 items. The Goods and Services Tax Council has earlier set rates - ranging from 5 per cent to 28 per cent - for a multitude of goods and services under GST.
Goods and services tax is a single tax to promote trade and industry, replacing multiple levies from the manufacturer to supplier to customer, according to the Central Board of Excise and Customs (CBEC) website. It will give a fillip to making India a manufacturing hub, creating a unified common national market, boosting investments and exports, and generating more employment, the CBEC said. The GST will subsume a number of central taxes - such as central excise duty and service tax - and state levies - including VAT, luxury tax, and entertainment tax.
The GST will subsume a number of central taxes - such as central excise duty and service tax - and state levies - including VAT, luxury tax, and entertainment tax.
Here are a few taxes that will be subsumed in GST:
Central sales tax
Central sales tax or CST is the tax levied on sale of items in inter-state trade. An origin-based tax, CST is charged where the item is sold.
Subsuming of CST, besides major central and state taxes, in GST, is expected to reduce the cost of locally manufactured goods and services.
Service tax
Service tax is the tax payable on services that are taxable. While in most cases, the service provider is liable to pay this tax, in certain cases the recipient of the service is liable to pay tax. This is known as the reverse charge mechanism.
Octroi
Octroi, commonly referred to as "entry tax", is the local tax paid on consumables brought to a state at the time of entry.
Special additional duty of customs
SAD or Special Additional Duty is the duty paid on the imported goods. The importer could claim for the refund of the special additional duty after the subsequent sale of the imported items.
Additional excise duty
This is the duty charged on certain goods which are produced, manufactured or stored in the country.
Countervailing duty
This is a type of duty import tax applicable on certain goods in order to prevent dumping or counter export subsidies.
Purchase tax
Unlike sales tax, which is paid by the seller, this tax is paid by the consumer on purchase of a good. In practice, the seller usually passes on the sales tax to the purchaser in the form of higher price for an item.
Entertainment tax
This tax includes exhibition, performance, amusement, game, sport or race (including horse race) and exhibitions of films. Proprietors or organisers of entertainment are liabile to collect entertainment tax from the consumers and pass on the same to the government.
Central Excise duty
This form of indirect tax is levied on goods and commodities manufactured within the country.
State VAT
Value added tax or VAT is the tax applicable on addition of value. Collected at different stages of sale, VAT is a consumption tax that is placed on a product whenever value is added at different stages of production.
Goods and services tax is a single tax to promote trade and industry, replacing multiple levies from the manufacturer to supplier to customer, according to the Central Board of Excise and Customs (CBEC) website. It will give a fillip to making India a manufacturing hub, creating a unified common national market, boosting investments and exports, and generating more employment, the CBEC said.
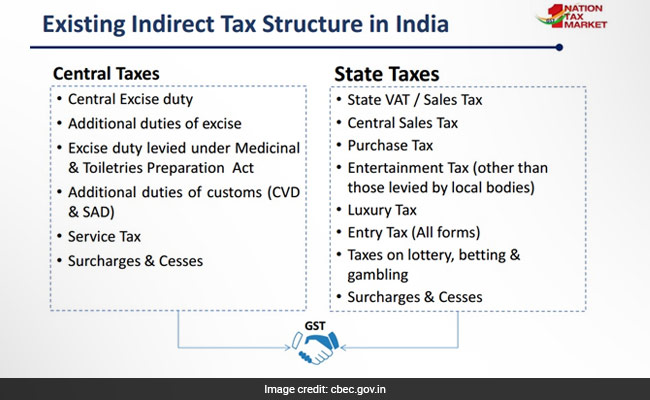
Here are a few taxes that will be subsumed in GST:
Central sales tax
Central sales tax or CST is the tax levied on sale of items in inter-state trade. An origin-based tax, CST is charged where the item is sold.
Subsuming of CST, besides major central and state taxes, in GST, is expected to reduce the cost of locally manufactured goods and services.
Service tax
Service tax is the tax payable on services that are taxable. While in most cases, the service provider is liable to pay this tax, in certain cases the recipient of the service is liable to pay tax. This is known as the reverse charge mechanism.
Octroi
Octroi, commonly referred to as "entry tax", is the local tax paid on consumables brought to a state at the time of entry.
Special additional duty of customs
SAD or Special Additional Duty is the duty paid on the imported goods. The importer could claim for the refund of the special additional duty after the subsequent sale of the imported items.
Additional excise duty
This is the duty charged on certain goods which are produced, manufactured or stored in the country.
Countervailing duty
This is a type of duty import tax applicable on certain goods in order to prevent dumping or counter export subsidies.
Purchase tax
Unlike sales tax, which is paid by the seller, this tax is paid by the consumer on purchase of a good. In practice, the seller usually passes on the sales tax to the purchaser in the form of higher price for an item.
Entertainment tax
This tax includes exhibition, performance, amusement, game, sport or race (including horse race) and exhibitions of films. Proprietors or organisers of entertainment are liabile to collect entertainment tax from the consumers and pass on the same to the government.
Central Excise duty
This form of indirect tax is levied on goods and commodities manufactured within the country.
State VAT
Value added tax or VAT is the tax applicable on addition of value. Collected at different stages of sale, VAT is a consumption tax that is placed on a product whenever value is added at different stages of production.
Track Latest News Live on NDTV.com and get news updates from India and around the world

