ISRO's PSLV C-15 launch successful
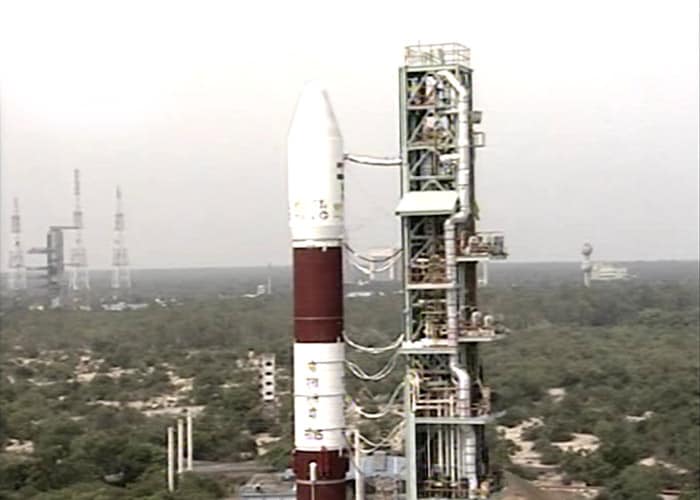
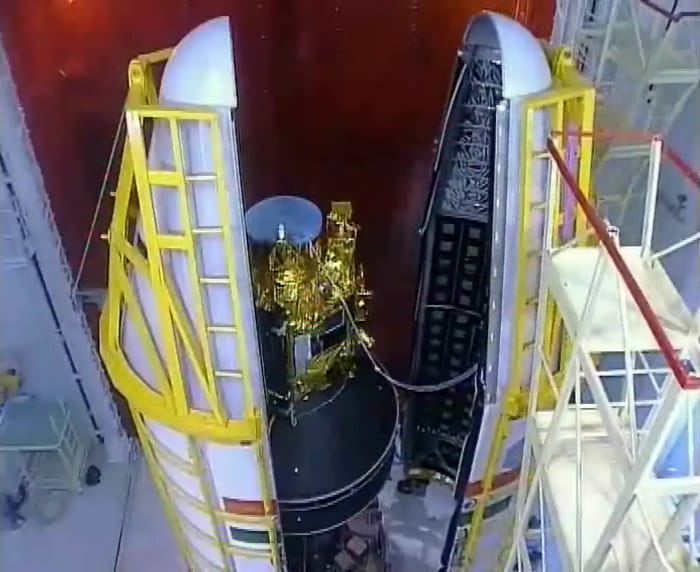
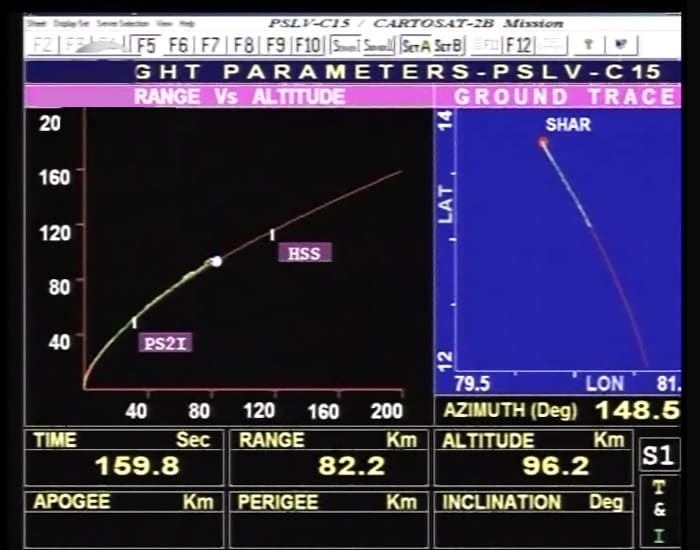
In a textbook launch, India's Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV) successfully placed into orbit remote sensing satellite Cartosat-2B and four other satellites after a perfect lift off from the Sriharikota spaceport on Monday.
-
In a textbook launch, India's Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV) successfully placed into orbit remote sensing satellite Cartosat-2B and four other satellites after a perfect lift off from the Sriharikota spaceport on Monday.
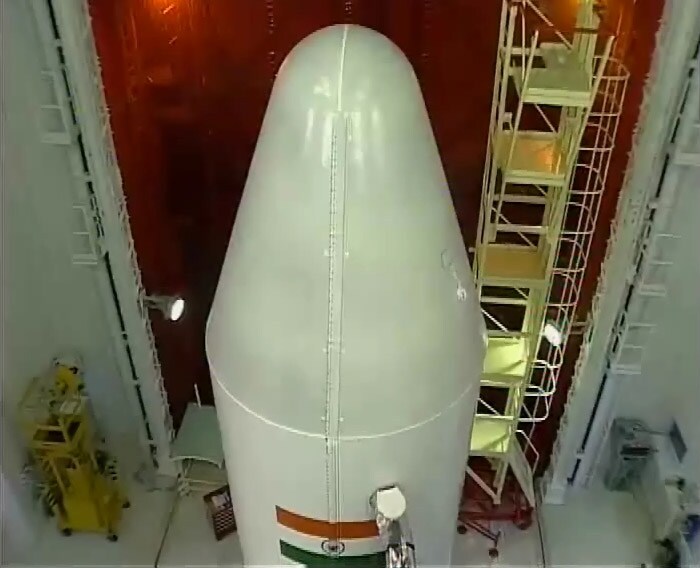
At the end of an over 51-hour countdown, the 44.4 metre-tall four-stage PSLV-C-15, costing Rs 260 crore, blasted off from a launch pad at the Satish Dhawan Space Centre with ignition of the core first stage and placed the satellites in orbit one after the other. -
The PSLV launch assumes significance as it comes about three months after ISRO suffered a major setback on April 15 when the Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle (GSLV-D3), which was launched using an Indian-designed and built cryogenic engine for the first time, failed and fell into the Bay of Bengal.
-
Cartosat-2B is mainly intended to augment remote sensing data services to the users of multiple spot scene imagery with 0.8 metre spatial resolution and 9.6 km swath in the panchromatic.
Cartosat-2 and 2A, two Indian remote sensing satellites in orbit, are currently providing such services. -
A set of four satellites including Studsat built by students of seven engineering colleges in Andhra Pradesh and Karnataka, Alsat from Algeria, two nano satellites from Canada and Switzerland, and a pico (very small) satellite called Oceansat 2 accompanied Cartosat 2 on its trip to orbit.