ISRO's PSLV C-15 launch successful
In a textbook launch, India's Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV) successfully placed into orbit remote sensing satellite Cartosat-2B and four other satellites after a perfect lift off from the Sriharikota spaceport on Monday.
-
 In a textbook launch, India's Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV) successfully placed into orbit remote sensing satellite Cartosat-2B and four other satellites after a perfect lift off from the Sriharikota spaceport on Monday.
In a textbook launch, India's Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV) successfully placed into orbit remote sensing satellite Cartosat-2B and four other satellites after a perfect lift off from the Sriharikota spaceport on Monday.
At the end of an over 51-hour countdown, the 44.4 metre-tall four-stage PSLV-C-15, costing Rs 260 crore, blasted off from a launch pad at the Satish Dhawan Space Centre with ignition of the core first stage and placed the satellites in orbit one after the other. -
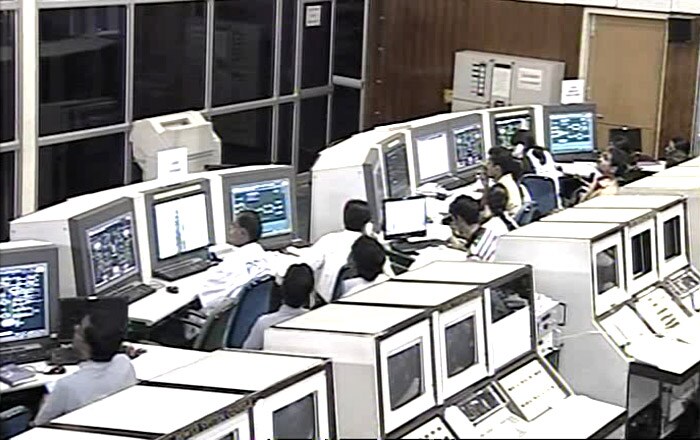 Visibly relieved scientists, headed by ISRO chairman Dr K Radhakrishnan, cheered as ISRO's workhorse PSLV soared into clear skies at 9.22 am.
Visibly relieved scientists, headed by ISRO chairman Dr K Radhakrishnan, cheered as ISRO's workhorse PSLV soared into clear skies at 9.22 am. -
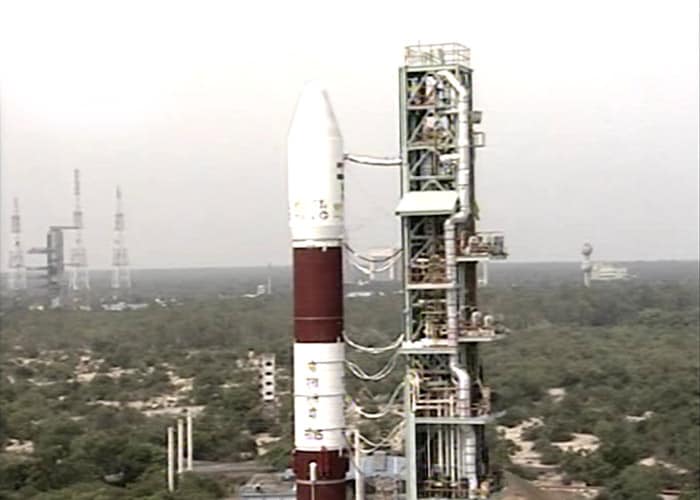 The PSLV launch assumes significance as it comes about three months after ISRO suffered a major setback on April 15 when the Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle (GSLV-D3), which was launched using an Indian-designed and built cryogenic engine for the first time, failed and fell into the Bay of Bengal.
The PSLV launch assumes significance as it comes about three months after ISRO suffered a major setback on April 15 when the Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle (GSLV-D3), which was launched using an Indian-designed and built cryogenic engine for the first time, failed and fell into the Bay of Bengal. -
 Besides launching 17 Indian satellites, PSLV has also launched 22 foreign satellites during 1994-2009 into polar sun synchronous, geosynchronous transfer, highly elliptical and low earth orbits and has repeatedly proved its reliability and versatility.
Besides launching 17 Indian satellites, PSLV has also launched 22 foreign satellites during 1994-2009 into polar sun synchronous, geosynchronous transfer, highly elliptical and low earth orbits and has repeatedly proved its reliability and versatility. -
 Cartosat-2B is an advanced remote sensing satellite built by ISRO. This is the latest in the Indian remote sensing satellite series and the 17th in this series.
Cartosat-2B is an advanced remote sensing satellite built by ISRO. This is the latest in the Indian remote sensing satellite series and the 17th in this series. -
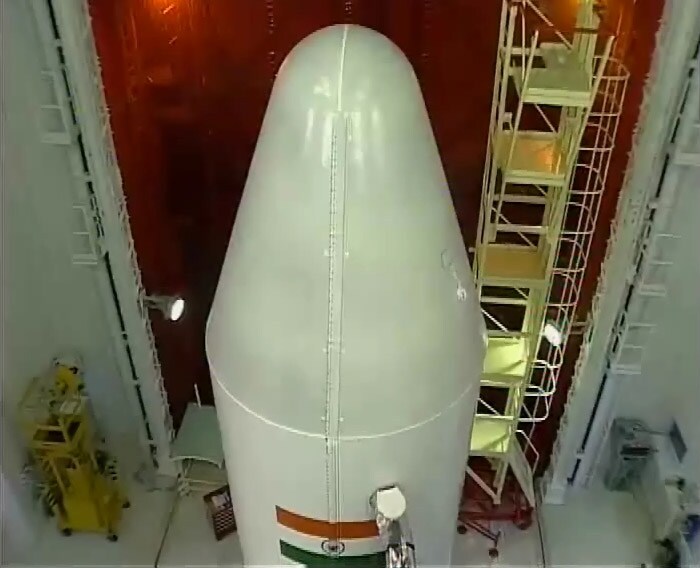 Cartosat-2B is mainly intended to augment remote sensing data services to the users of multiple spot scene imagery with 0.8 metre spatial resolution and 9.6 km swath in the panchromatic.
Cartosat-2B is mainly intended to augment remote sensing data services to the users of multiple spot scene imagery with 0.8 metre spatial resolution and 9.6 km swath in the panchromatic.
Cartosat-2 and 2A, two Indian remote sensing satellites in orbit, are currently providing such services. -
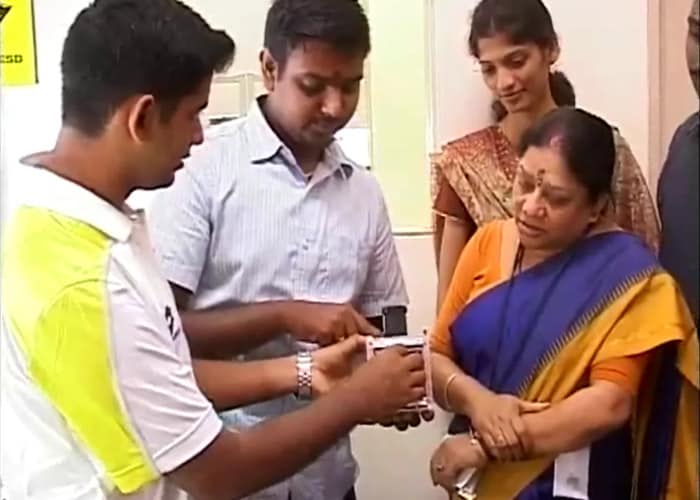 A set of four satellites including Studsat built by students of seven engineering colleges in Andhra Pradesh and Karnataka, Alsat from Algeria, two nano satellites from Canada and Switzerland, and a pico (very small) satellite called Oceansat 2 accompanied Cartosat 2 on its trip to orbit.
A set of four satellites including Studsat built by students of seven engineering colleges in Andhra Pradesh and Karnataka, Alsat from Algeria, two nano satellites from Canada and Switzerland, and a pico (very small) satellite called Oceansat 2 accompanied Cartosat 2 on its trip to orbit. -
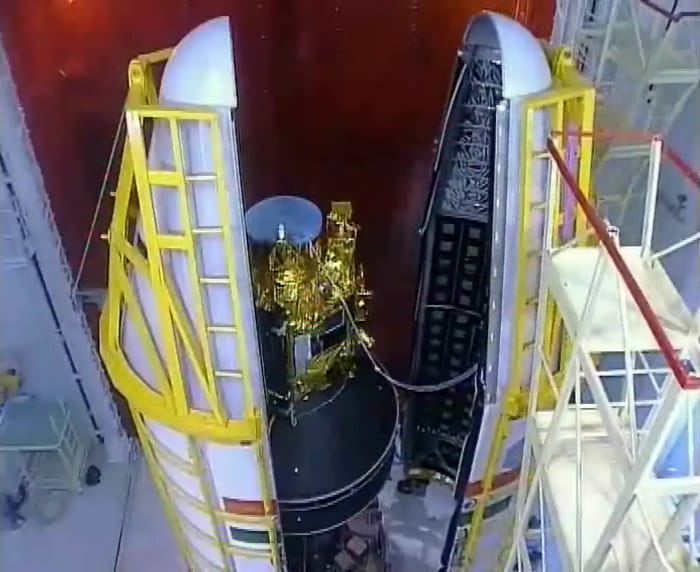 Alsat from Algeria, weighing 116 kg, is also a remote sensing satellite. The two nano satellites, NLS 6.1 and NLS 6.2, weigh six kg and one kg each. Studsat weighs less than one kg.
Alsat from Algeria, weighing 116 kg, is also a remote sensing satellite. The two nano satellites, NLS 6.1 and NLS 6.2, weigh six kg and one kg each. Studsat weighs less than one kg.
Advertisement
Advertisement
Advertisement
