World Telecommunication Day: From Landline To Mobile, How Technology Changed
World Telecommunication Day is celebrated every year on May 17 since 1969. The date also marks the founding of International Telecommunication Union, a United Nations agency, on May 17, 1865.
-
 The purpose of World Telecommunication and Information Society Day (WTISD) is to help raise awareness of the possibilities that the use of the internet and other information and communication technologies can bring to societies and economies, as well as of ways to bridge the digital divide. (Pixabay)
The purpose of World Telecommunication and Information Society Day (WTISD) is to help raise awareness of the possibilities that the use of the internet and other information and communication technologies can bring to societies and economies, as well as of ways to bridge the digital divide. (Pixabay) -
 The event focuses on a particular theme for each event. In 2024, the theme is???????????????????????????????????????? Digital Innovation for Sustainable Development. (Unsplash)
The event focuses on a particular theme for each event. In 2024, the theme is???????????????????????????????????????? Digital Innovation for Sustainable Development. (Unsplash) -
 In the last 55 years, communication technology has undergone a radical transformation. What started with landline telephones has evolved through various stages to the high-speed, ubiquitous connectivity of 5G. This journey reflects not just technological advancements but also significant changes in how people interact, work and live. (Unsplash)
In the last 55 years, communication technology has undergone a radical transformation. What started with landline telephones has evolved through various stages to the high-speed, ubiquitous connectivity of 5G. This journey reflects not just technological advancements but also significant changes in how people interact, work and live. (Unsplash) -
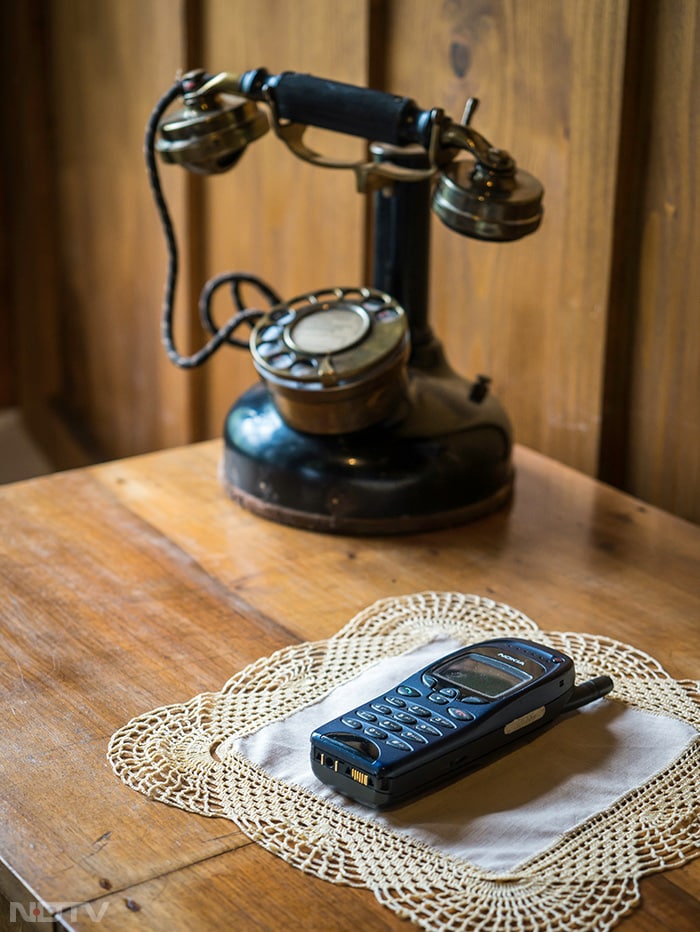 In the late 1960s and early 1970s, landline telephones were the cornerstone of communication. These devices, often rotary dial phones, were found in almost every household. They provided a reliable means of voice communication, connecting people over long distances through a vast network of wired infrastructure. (Unsplash)
In the late 1960s and early 1970s, landline telephones were the cornerstone of communication. These devices, often rotary dial phones, were found in almost every household. They provided a reliable means of voice communication, connecting people over long distances through a vast network of wired infrastructure. (Unsplash) -
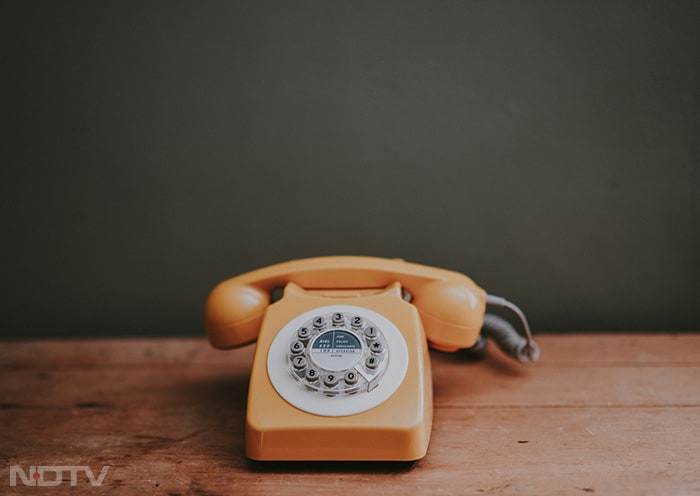 The introduction of touch-tone dialing in the 1970s marked a significant improvement, allowing faster and more convenient dialing. However, the fundamental limitation remained: Mobility was non-existent. Communication was tethered to a specific location, usually the home or office. (Unsplash)
The introduction of touch-tone dialing in the 1970s marked a significant improvement, allowing faster and more convenient dialing. However, the fundamental limitation remained: Mobility was non-existent. Communication was tethered to a specific location, usually the home or office. (Unsplash) -
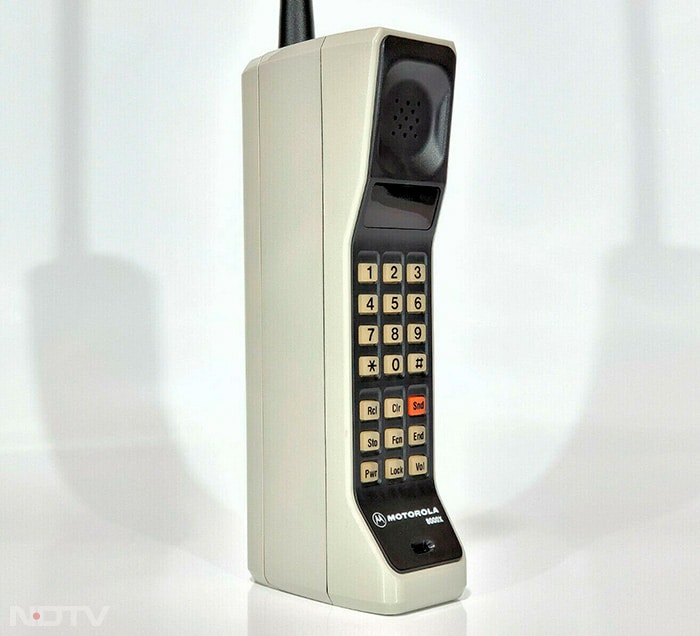 The 1990s saw the birth of mobile phones, beginning with the bulky, expensive models like the Motorola DynaTAC. These early mobile phones were primarily status symbols, limited to a small segment of the population due to their high cost and the nascent stage of cellular networks. (X/@OnThisDayHisto)
The 1990s saw the birth of mobile phones, beginning with the bulky, expensive models like the Motorola DynaTAC. These early mobile phones were primarily status symbols, limited to a small segment of the population due to their high cost and the nascent stage of cellular networks. (X/@OnThisDayHisto) -
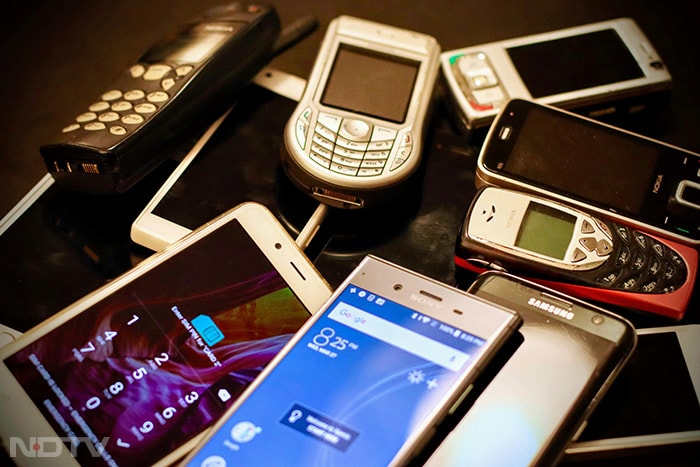 As technology progressed, phones became smaller, more affordable, and widely available. By late 1990s and early 2000s, the second generation of mobile technology introduced digital encryption, SMS and basic internet capabilities, marking a significant leap forward. (Unsplash)
As technology progressed, phones became smaller, more affordable, and widely available. By late 1990s and early 2000s, the second generation of mobile technology introduced digital encryption, SMS and basic internet capabilities, marking a significant leap forward. (Unsplash) -
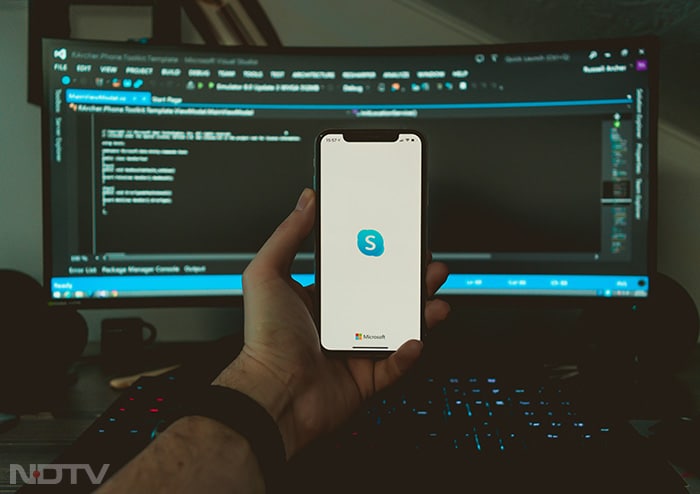 Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) technology, introduced by services such as Skype in 2003, began to challenge traditional telephony. VoIP allowed voice communication over the internet, significantly reducing the cost of long-distance and international calls. (Unsplash)
Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) technology, introduced by services such as Skype in 2003, began to challenge traditional telephony. VoIP allowed voice communication over the internet, significantly reducing the cost of long-distance and international calls. (Unsplash) -
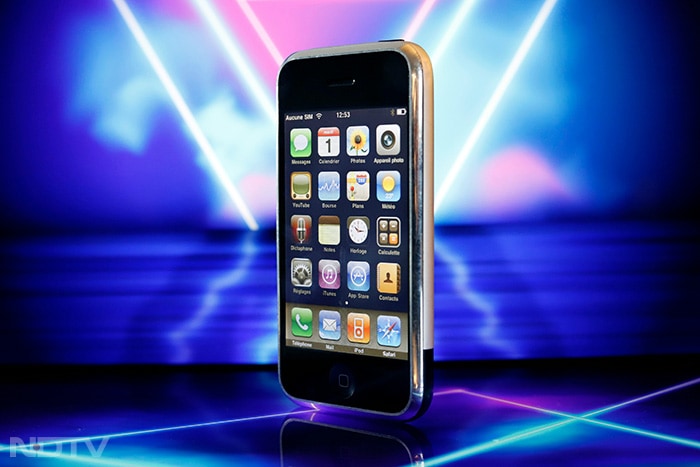 The introduction of the iPhone in 2007 by Apple marked the beginning of the smartphone era. Smartphones combined mobile phone capabilities with powerful computing features, effectively putting a mini-computer in every user's pocket. The subsequent release of Android further popularised smartphones, making them accessible to a broader audience. (Unsplash)
The introduction of the iPhone in 2007 by Apple marked the beginning of the smartphone era. Smartphones combined mobile phone capabilities with powerful computing features, effectively putting a mini-computer in every user's pocket. The subsequent release of Android further popularised smartphones, making them accessible to a broader audience. (Unsplash) -
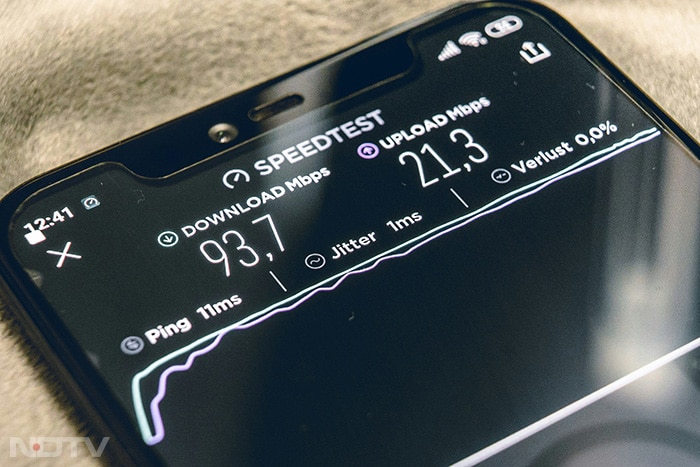 The rollout of 4G LTE networks in 2010s brought significant improvements in speed and reliability. 4G enabled high-definition video streaming, seamless video calls and faster internet browsing on mobile devices, enhancing both personal and professional communication. (Unsplash)
The rollout of 4G LTE networks in 2010s brought significant improvements in speed and reliability. 4G enabled high-definition video streaming, seamless video calls and faster internet browsing on mobile devices, enhancing both personal and professional communication. (Unsplash) -
 As the demand for faster and more reliable communication grew, the development of 5G technology began. 5G, launched in early 2020s, promised even greater speeds, lower latency, and the ability to connect a vast number of devices simultaneously. This advancement is not just about speed but also about enabling new technologies such as the Internet of Things (IoT), augmented reality (AR) and autonomous vehicles. (Unsplash)
As the demand for faster and more reliable communication grew, the development of 5G technology began. 5G, launched in early 2020s, promised even greater speeds, lower latency, and the ability to connect a vast number of devices simultaneously. This advancement is not just about speed but also about enabling new technologies such as the Internet of Things (IoT), augmented reality (AR) and autonomous vehicles. (Unsplash)
Advertisement
Advertisement
Advertisement
Advertisement
