
The Pakistan army garrison at Sargodha.
Pakistan has a nuclear stockpile of between 130 and 140 nuclear warheads, according to a group of American scientists, whose tally is partially based on close scrutiny of satellite images and matches other recent estimates. Their report also reiterates that in violation of the US' guidelines, Pakistan has converted its F-16 fighter jets for use with nuclear weapons. In addition to this, "French-produced Mirage aircraft are widely assumed to be equipped to deliver the Raad air-launched cruise missile.''
The report indicates that a detachment of Pakistani air force fighters capable of delivering nuclear warheads are housed at the Masroor Air Base west of Karachi which offers ''a large underground facility that is located inside a high-security area. The underground facility is possibly a command center."
 Pakistani's primary means of delivering nuclear weapons, however, are through cruise and ballistic missile systems. The report, titled "Pakistan's Evolving Nuclear Weapons Infrastructure", has used commercially-available satellite images to identify ten Pakistani facilities, including five missile garrisons and at least two air bases, which have been used to assemble and house nuclear missile launchers.
Pakistani's primary means of delivering nuclear weapons, however, are through cruise and ballistic missile systems. The report, titled "Pakistan's Evolving Nuclear Weapons Infrastructure", has used commercially-available satellite images to identify ten Pakistani facilities, including five missile garrisons and at least two air bases, which have been used to assemble and house nuclear missile launchers.
Hans M Kristensen, a top scientist at FAS, said, ''Analysis of commercial satellite photos has identified features that suggest that at least five bases might serve a role in Pakistan's emerging nuclear posture. This includes army garrisons at Akro [Sindh], Gujranwala [Punjab], Khuzdar [Balochistan], Pano Aqil [Sindh], and Sargodha. A sixth base at Bahawalpur may be under construction. There is also a seventh base near Dera Ghazi Khan, but the infrastructure is very different and not yet convincing."
 The satellite images indicate the presence of vehicles associated with nuclear-capable missiles which can strike targets ranging from a relatively close distance of less than 100 kms to others of an intermediate range which can target most areas in India and employ technology and components transferred to Pakistan from China.
The satellite images indicate the presence of vehicles associated with nuclear-capable missiles which can strike targets ranging from a relatively close distance of less than 100 kms to others of an intermediate range which can target most areas in India and employ technology and components transferred to Pakistan from China.
The report also concludes that a string of facilities west of Islamabad, which comprise the Pakistani National Development Complex, are key to producing Shaheen-2 medium-range ballistic missile launchers and Babur ground-launched cruise missile launchers.
 The report concludes that Pakistan's nuclear arsenal remains in a ''dynamic phase'' though Islamabad "might not intend to continue to increase its arsenal indefinitely but may soon reach the goal for the size of its full-spectrum deterrent.'' Essentially, that Pakistan's nuclear weapons programme is growing, meeting the country's requirements and acting as a full-fledged deterrent against India.
The report concludes that Pakistan's nuclear arsenal remains in a ''dynamic phase'' though Islamabad "might not intend to continue to increase its arsenal indefinitely but may soon reach the goal for the size of its full-spectrum deterrent.'' Essentially, that Pakistan's nuclear weapons programme is growing, meeting the country's requirements and acting as a full-fledged deterrent against India.
The report indicates that a detachment of Pakistani air force fighters capable of delivering nuclear warheads are housed at the Masroor Air Base west of Karachi which offers ''a large underground facility that is located inside a high-security area. The underground facility is possibly a command center."
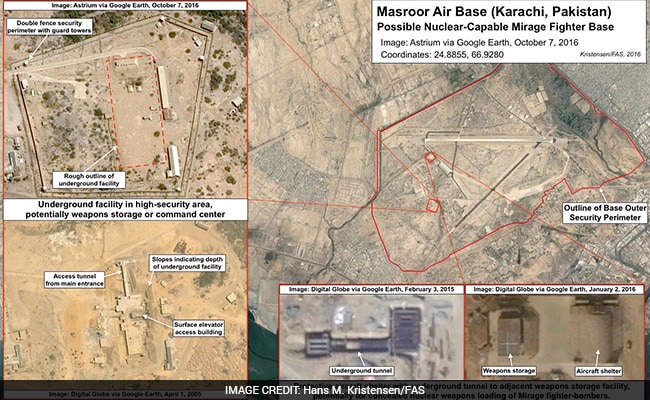
The Masroor Air Base, west of Karachi.
Hans M Kristensen, a top scientist at FAS, said, ''Analysis of commercial satellite photos has identified features that suggest that at least five bases might serve a role in Pakistan's emerging nuclear posture. This includes army garrisons at Akro [Sindh], Gujranwala [Punjab], Khuzdar [Balochistan], Pano Aqil [Sindh], and Sargodha. A sixth base at Bahawalpur may be under construction. There is also a seventh base near Dera Ghazi Khan, but the infrastructure is very different and not yet convincing."
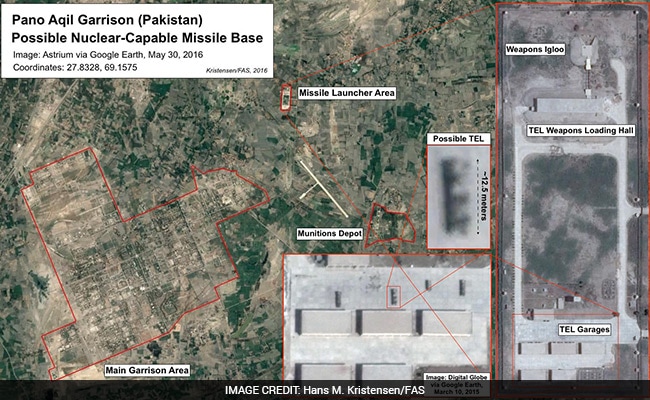
The army garrison at Pano Aqil.
The report also concludes that a string of facilities west of Islamabad, which comprise the Pakistani National Development Complex, are key to producing Shaheen-2 medium-range ballistic missile launchers and Babur ground-launched cruise missile launchers.
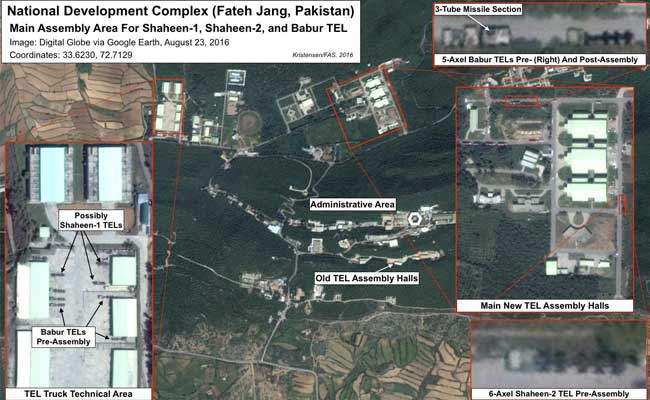
The Pakistani National Development Complex which is located west of Islamabad.
Track Latest News Live on NDTV.com and get news updates from India and around the world

